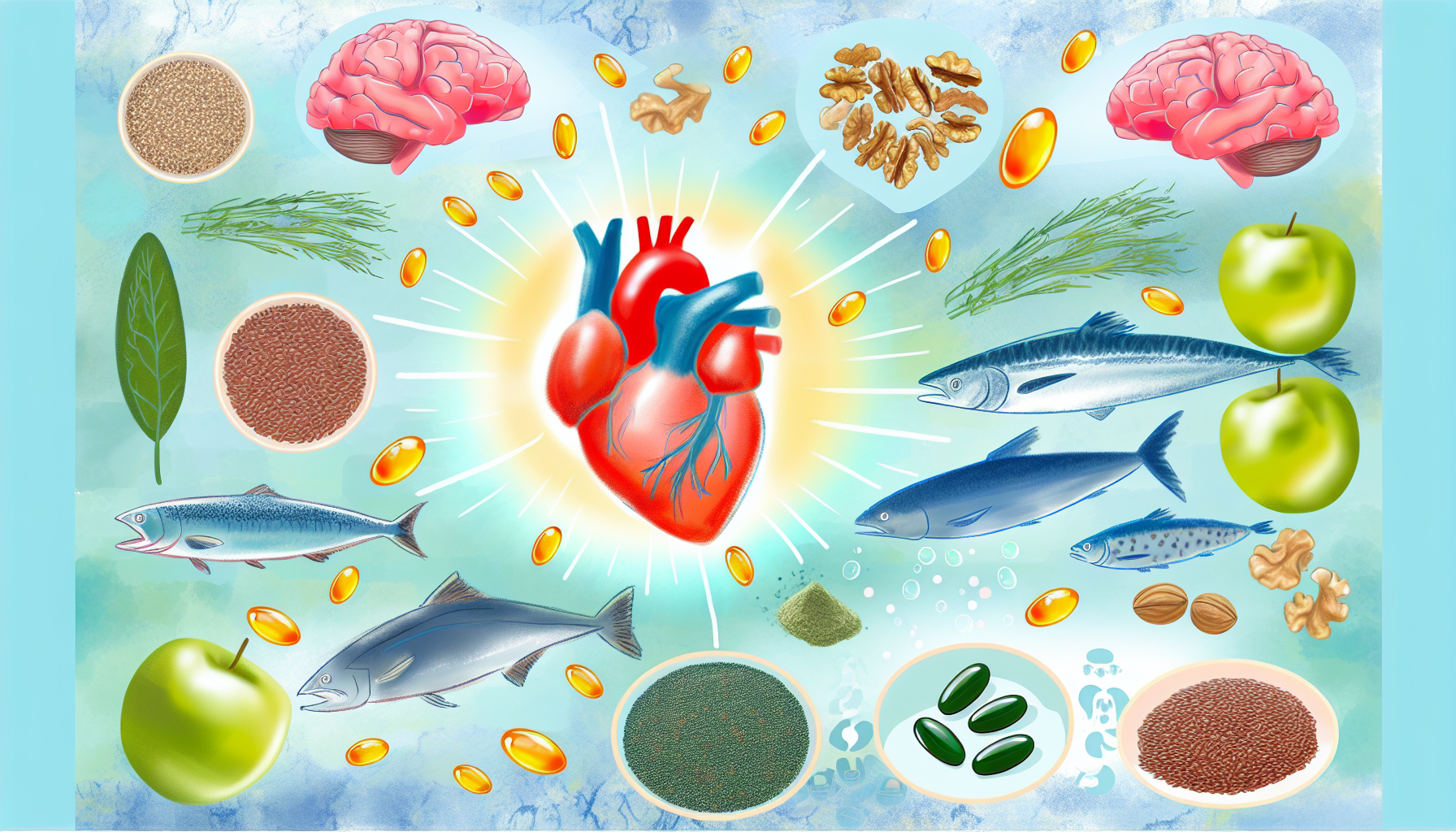
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential to our health and are recognized for their many benefits in preventing chronic diseases. These polyunsaturated fatty acids play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. In this article, we will explore in depth the importance of omega-3 for our body, based on the latest scientific research.
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning our bodies cannot produce them and must be obtained through diet. There are three main types of omega-3: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found primarily in plant sources such as flaxseed, walnuts, and vegetable oils, while EPA and DHA are found primarily in oily fish and algae.
Reduction of inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a common risk factor for many chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and some forms of cancer. Omega-3s have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. EPA and DHA, in particular, have been shown to reduce the production of molecules and substances linked to inflammation, such as inflammatory cytokines.
The anti-inflammatory mechanisms of omega-3
Omega-3s modulate inflammation by influencing cell membranes and regulating the production of eicosanoids, compounds involved in the inflammatory response. Omega-3s also inhibit enzymes responsible for inflammation and promote the production of resolvins and protectins, molecules that contribute to the resolution of inflammation.
Improved cardiovascular health
The cardiovascular health benefits of omega-3s are well documented. These fatty acids help reduce triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and improve endothelial function.
Reduce triglycerides and blood pressure
Studies have shown that consuming EPA and DHA can reduce blood triglyceride levels, which lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease. Omega-3s also help lower blood pressure, especially in people with hypertension, by promoting vasodilation and increasing the flexibility of blood vessels.
Prevention of neurodegenerative diseases
Omega-3s, especially DHA, play a vital role in brain health. They contribute to the structure of neuronal cell membranes and have neuroprotective properties.
Protection against dementia and Alzheimer's disease
Research has suggested that adequate levels of omega-3s may be associated with a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. Omega-3s can improve the fluidity of neuronal membranes, promote communication between brain cells, and reduce oxidative damage and inflammation.
Prevention of autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by an aberrant immune response against the person’s own body tissues. Omega-3s may help modulate the immune response and reduce symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
Omega-3 and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Studies have shown that omega-3 supplements can reduce symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease. This reduction in symptoms is mainly due to the anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3s, which reduce joint pain and swelling.
Food sources of omega-3
To benefit from the benefits of omega-3s, it is essential to include them in our daily diet. Here are some of the best food sources of omega-3s:
Fatty fish
Oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines and herring are rich in EPA and DHA. It is recommended to consume oily fish twice a week to obtain adequate levels of omega-3.
Flax seeds
Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil are excellent sources of ALA, a precursor to omega-3s. You can add ground flaxseeds to your cereal, yogurt, or salads to increase your omega-3 intake.
Nut
Walnuts are another plant source of ALA. They can be eaten as a snack or added to dishes to reap their health benefits.
Algae
Algae and algae oil supplements are non-animal sources of EPA and DHA. They are especially useful for vegans and vegetarians.
Omega-3 Supplements
If you have difficulty getting enough omega-3s through diet, you may want to consider taking supplements. When choosing omega-3 supplements, it is important to select quality products to avoid contaminants such as heavy metals.
How to Choose Quality Supplements
Look for supplements that have been third-party tested to ensure their purity and potency. Opt for high-quality fish oils, preferably those labeled “concentrated” for higher EPA and DHA content.